The thread title, which is heavily used in the thread "Why do they hate being called Christians" is not in violation of the rules, so it seems. I am critiquing a book, not a denomination, unlike certain members who mindlessly bash and insult with rule immunity.
Some anti-Catholics claim the Catholic Church is the Whore of Babylon of Revelation 17 and 18. Dave Hunt, in his 1994 book, A Woman Rides the Beast, presents nine arguments to try to prove this. His claims are a useful summary of those commonly used by Fundamentalists, and an examination of them shows why they don’t work.
Hunt argues that the Whore "is a city built on seven hills," which he identifies as the seven hills of ancient Rome. This argument is based on Revelation 17:9, which states that the woman sits on seven mountains.
Vatican City is not built on seven hills, but only one: Vatican Hill, which is not one of the seven upon which ancient Rome was built. Those hills are on the east side of the Tiber river; Vatican Hill is on the west.
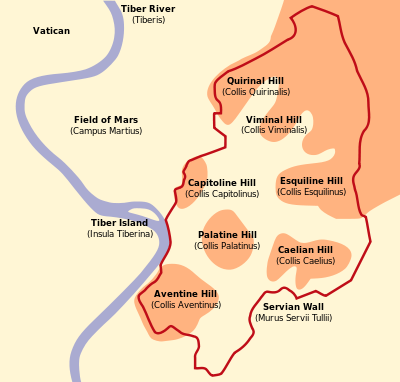
It's not even close.
#2: "Babylon"—What’s in a Name?
Hunt notes that the Whore will be a city "known as Babylon." This is based on Revelation 17:5, which says that her name is "Babylon the Great."
The phrase "Babylon the great" (Greek: Babulon a megala) occurs five times in Revelation (14:8, 16:19, 17:5, 18:2, and 18:21). Light is shed on its meaning when one notices that Babylon is referred to as "the great city" seven times in the book (16:19, 17:18, 18:10, 16, 18, 19, 21). Other than these, there is only one reference to "the great city." That passage is 11:8, which states that the bodies of God’s two witnesses "will lie in the street of the great city, which is allegorically called Sodom and Egypt, where their Lord was crucified."
"The great city" is symbolically called Sodom, a reference to Jerusalem, symbolically called "Sodom" in the Old Testament (cf. Is. 1:10; Ezek. 16:1–3, 46–56). We also know Jerusalem is the "the great city" of Revelation 11:8 because the verse says it was "where [the] Lord was crucified."
Revelation consistently speaks as if there were only one "great city" ("the great city"), suggesting that the great city of 11:8 is the same as the great city mentioned in the other seven texts—Babylon. Additional evidence for the identity of the two is the fact that both are symbolically named after great Old Testament enemies of the faith: Sodom, Egypt, and Babylon.
This suggests that Babylon the great may be Jerusalem, not Rome. Many Protestant and Catholic commentators have adopted this interpretation. On the other hand, early Church Fathers often referred to Rome as "Babylon," but every references was to pagan Rome, which martyred Christians.
#3: Commits Fornication
Hunt tells us, "The woman is called a ‘whore’ (verse 1), with whom earthly kings ‘have committed fornication’ (verse 2). Against only two cities could such a charge be made: Jerusalem and Rome."
Here Hunt admits that the prophets often referred to Jerusalem as a spiritual whore, suggesting that the Whore might be apostate Jerusalem. Ancient, pagan Rome also fits the description, since through the cult of emperor worship it also committed spiritual fornication with "the kings of the earth" (those nations it conquered).
To identify the Whore as Vatican City, Hunt interprets the fornication as alleged "unholy alliances" forged between Vatican City and other nations, but he fails to cite any reasons why the Vatican’s diplomatic relations with other nations are "unholy."
He also confuses Vatican City with the city of Rome, and he neglects the fact that pagan Rome had "unholy alliances" with the kingdoms it governed (unholy because they were built on paganism and emperor worship).
#4: Clothed in Purple and Red
Hunt states, "She [the Whore] is clothed in ‘purple and scarlet’ (verse 4), the colors of the Catholic clergy." He then cites the Catholic Encyclopedia to show that bishops wear certain purple vestments and cardinals wear certain red vestments.
Hunt ignores the obvious symbolic meaning of the colors—purple for royalty and red for the blood of Christian martyrs. Instead, he is suddenly literal in his interpretation. He understood well enough that the woman symbolizes a city and that the fornication symbolizes something other than literal sex, but now he wants to assign the colors a literal, earthly fulfillment in a few vestments of certain Catholic clergy.
Purple and red are not the dominant colors of Catholic clerical vestments. White is. All priests wear white (including bishops and cardinals when they are saying Mass)—even the pope does so.
The purple and scarlet of the Whore are contrasted with the white of the New Jerusalem, the Bride of Christ (Rev. 19:8). This is a problem for Hunt for three reasons:
(a) we have already noted that the dominant color of Catholic clerical vestments is white, which would identify them with New Jerusalem if the color is taken literally;
(b the clothing of the Bride is given a symbolic interpretation ("the righteous acts of the saints;" 19:8); implying that the clothing of the Whore should also be given a symbolic meaning; and
(c) the identification of the Bride as New Jerusalem (Rev. 3:12, 21:2, 10) suggests that the Whore may be old (apostate) Jerusalem—a contrast used elsewhere in Scripture (Gal. 4:25–26).
Hunt ignores the liturgical meaning of purple and red in Catholic symbolism. Purple symbolizes repentance, and red honors the blood of Christ and the Christian martyrs.
It is appropriate for Catholic clerics to wear purple and scarlet, if for no other reason because they have been liturgical colors of the true religion since ancient Israel.
Hunt neglects to remind his readers that God commanded that scarlet yarn and wool be used in liturgical ceremonies (Lev. 14:4, 6, 49–52; Num. 19:6), and that God commanded that the priests’ vestments be made with purple and scarlet yarn (Ex. 28:4–8, 15, 33, 39:1–8, 24, 29).
#5: Possesses Great Wealth
Hunt states, "[The Whore’s] incredible wealth next caught John’s eye. She was ‘decked with gold and precious stones and pearls . . . ’ [Rev. 17:4]." The problem is that, regardless of what it had in the past, the modern Vatican is not fantastically wealthy. In fact, it has run a budget deficit in most recent years and has an annual budget only around the size of that of the Archdiocese of Chicago. Furthermore, wealth was much more in character with pagan Rome or apostate Jerusalem, both key economic centers.
Some anti-Catholics claim the Catholic Church is the Whore of Babylon of Revelation 17 and 18. Dave Hunt, in his 1994 book, A Woman Rides the Beast, presents nine arguments to try to prove this. His claims are a useful summary of those commonly used by Fundamentalists, and an examination of them shows why they don’t work.
Hunt argues that the Whore "is a city built on seven hills," which he identifies as the seven hills of ancient Rome. This argument is based on Revelation 17:9, which states that the woman sits on seven mountains.
Vatican City is not built on seven hills, but only one: Vatican Hill, which is not one of the seven upon which ancient Rome was built. Those hills are on the east side of the Tiber river; Vatican Hill is on the west.

It's not even close.
#2: "Babylon"—What’s in a Name?
Hunt notes that the Whore will be a city "known as Babylon." This is based on Revelation 17:5, which says that her name is "Babylon the Great."
The phrase "Babylon the great" (Greek: Babulon a megala) occurs five times in Revelation (14:8, 16:19, 17:5, 18:2, and 18:21). Light is shed on its meaning when one notices that Babylon is referred to as "the great city" seven times in the book (16:19, 17:18, 18:10, 16, 18, 19, 21). Other than these, there is only one reference to "the great city." That passage is 11:8, which states that the bodies of God’s two witnesses "will lie in the street of the great city, which is allegorically called Sodom and Egypt, where their Lord was crucified."
"The great city" is symbolically called Sodom, a reference to Jerusalem, symbolically called "Sodom" in the Old Testament (cf. Is. 1:10; Ezek. 16:1–3, 46–56). We also know Jerusalem is the "the great city" of Revelation 11:8 because the verse says it was "where [the] Lord was crucified."
Revelation consistently speaks as if there were only one "great city" ("the great city"), suggesting that the great city of 11:8 is the same as the great city mentioned in the other seven texts—Babylon. Additional evidence for the identity of the two is the fact that both are symbolically named after great Old Testament enemies of the faith: Sodom, Egypt, and Babylon.
This suggests that Babylon the great may be Jerusalem, not Rome. Many Protestant and Catholic commentators have adopted this interpretation. On the other hand, early Church Fathers often referred to Rome as "Babylon," but every references was to pagan Rome, which martyred Christians.
#3: Commits Fornication
Hunt tells us, "The woman is called a ‘whore’ (verse 1), with whom earthly kings ‘have committed fornication’ (verse 2). Against only two cities could such a charge be made: Jerusalem and Rome."
Here Hunt admits that the prophets often referred to Jerusalem as a spiritual whore, suggesting that the Whore might be apostate Jerusalem. Ancient, pagan Rome also fits the description, since through the cult of emperor worship it also committed spiritual fornication with "the kings of the earth" (those nations it conquered).
To identify the Whore as Vatican City, Hunt interprets the fornication as alleged "unholy alliances" forged between Vatican City and other nations, but he fails to cite any reasons why the Vatican’s diplomatic relations with other nations are "unholy."
He also confuses Vatican City with the city of Rome, and he neglects the fact that pagan Rome had "unholy alliances" with the kingdoms it governed (unholy because they were built on paganism and emperor worship).
#4: Clothed in Purple and Red
Hunt states, "She [the Whore] is clothed in ‘purple and scarlet’ (verse 4), the colors of the Catholic clergy." He then cites the Catholic Encyclopedia to show that bishops wear certain purple vestments and cardinals wear certain red vestments.
Hunt ignores the obvious symbolic meaning of the colors—purple for royalty and red for the blood of Christian martyrs. Instead, he is suddenly literal in his interpretation. He understood well enough that the woman symbolizes a city and that the fornication symbolizes something other than literal sex, but now he wants to assign the colors a literal, earthly fulfillment in a few vestments of certain Catholic clergy.
Purple and red are not the dominant colors of Catholic clerical vestments. White is. All priests wear white (including bishops and cardinals when they are saying Mass)—even the pope does so.
The purple and scarlet of the Whore are contrasted with the white of the New Jerusalem, the Bride of Christ (Rev. 19:8). This is a problem for Hunt for three reasons:
(a) we have already noted that the dominant color of Catholic clerical vestments is white, which would identify them with New Jerusalem if the color is taken literally;
(b the clothing of the Bride is given a symbolic interpretation ("the righteous acts of the saints;" 19:8); implying that the clothing of the Whore should also be given a symbolic meaning; and
(c) the identification of the Bride as New Jerusalem (Rev. 3:12, 21:2, 10) suggests that the Whore may be old (apostate) Jerusalem—a contrast used elsewhere in Scripture (Gal. 4:25–26).
Hunt ignores the liturgical meaning of purple and red in Catholic symbolism. Purple symbolizes repentance, and red honors the blood of Christ and the Christian martyrs.
It is appropriate for Catholic clerics to wear purple and scarlet, if for no other reason because they have been liturgical colors of the true religion since ancient Israel.
Hunt neglects to remind his readers that God commanded that scarlet yarn and wool be used in liturgical ceremonies (Lev. 14:4, 6, 49–52; Num. 19:6), and that God commanded that the priests’ vestments be made with purple and scarlet yarn (Ex. 28:4–8, 15, 33, 39:1–8, 24, 29).
#5: Possesses Great Wealth
Hunt states, "[The Whore’s] incredible wealth next caught John’s eye. She was ‘decked with gold and precious stones and pearls . . . ’ [Rev. 17:4]." The problem is that, regardless of what it had in the past, the modern Vatican is not fantastically wealthy. In fact, it has run a budget deficit in most recent years and has an annual budget only around the size of that of the Archdiocese of Chicago. Furthermore, wealth was much more in character with pagan Rome or apostate Jerusalem, both key economic centers.


